Aperture refers to the adjustable opening in a camera lens that regulates how much light reaches the film or digital sensor. Measured in f-stops (e.g., f/1.4, f/8), it impacts both exposure and depth of field—making it one of the most powerful creative tools in cinematography.
How Aperture Works
-
Light Control
-
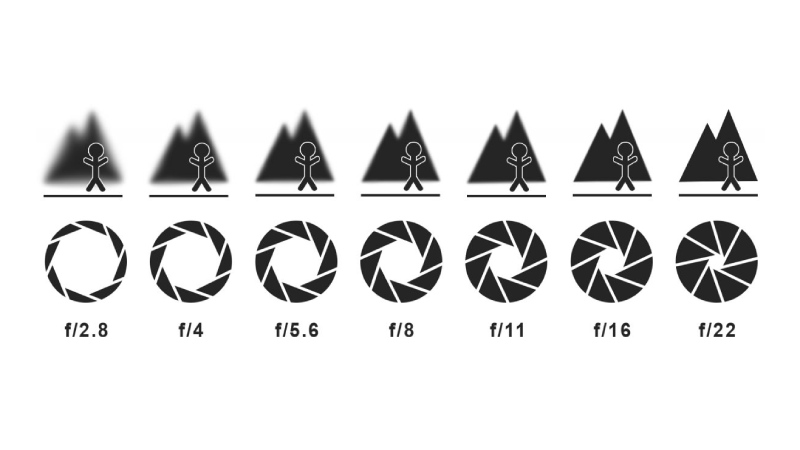
Wide aperture (low f-stop): More light enters (ideal for low-light scenes)
-
Narrow aperture (high f-stop): Less light enters (used in bright conditions)
-
-
Depth of Field
-
Shallow DOF (f/1.4): Blurred background, sharp subject (portraits, dramatic focus)
-
Deep DOF (f/16): Keeps foreground and background sharp (landscapes, surveillance shots)
-
Aperture in Filmmaking
-
Tonal Moods:
-
Film Noir: Wide apertures (f/2) for dark, moody scenes with selective focus
-
Epic Landscapes: Narrow apertures (f/11) for sweeping vistas (Lawrence of Arabia)
-
-
Bokeh Effects:
-
Creamy background blur (e.g., Citizen Kane’s deep focus vs. The Revenant’s shallow focus)
-
Technical Considerations
-
Lens Limitations: Cheaper lenses may lose sharpness at extreme apertures
-
T-Stops vs. F-Stops: Cinema lenses use T-stops (actual light transmission) for consistency
-
Diffraction: Over-narrow apertures (f/22+) reduce image clarity
Iconic Uses of Aperture
-
Moonlight (2016): Wide apertures for intimate close-ups
-
Blade Runner 2049 (2017): Mixed DOF to guide viewer attention
-
The Grand Budapest Hotel (2014): Deep focus for symmetrical compositions
Aperture Cheat Sheet
| f-stop | Use Case | Film Example |
|---|---|---|
| f/1.4 | Low-light, extreme bokeh | Nightcrawler (2014) |
| f/2.8 | Standard portraits | Her (2013) |
| f/8 | Group shots | The Social Network (2010) |
| f/16 | Landscape cinematography | Dune (2021) |
- Adventure Films | Film Terms Dictionary - August 1, 2025
- Korean Psychological Thriller “84 Jegopmiteo” Climbs to the Top of Netflix Charts - July 30, 2025
- Animation |Film Terms Dictionary - July 30, 2025
Aperture Film Terms Dictionary
Last modified: July 10, 2025






















